APQP
Definition
APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning) is the English term for (PQVP) Advance product quality planning and control plan or often also advance quality planning (QVP) called. QS-9000 is the standard set of norms and regulations that defines APQP. APQP is a defined process of advance quality planning that is used for the market launch of a new product or for the incorporation of changes to the product after its market launch.

History
APQP is based on the working group for supplier quality requirements (AIAG = Automotive Industry Action Group) created in 1982 by the three American car manufacturers Chrysler, General Motors and Ford. In 1992, a standardisation of the manuals took place. The result was the QS-9000 guidelines published in 1994.
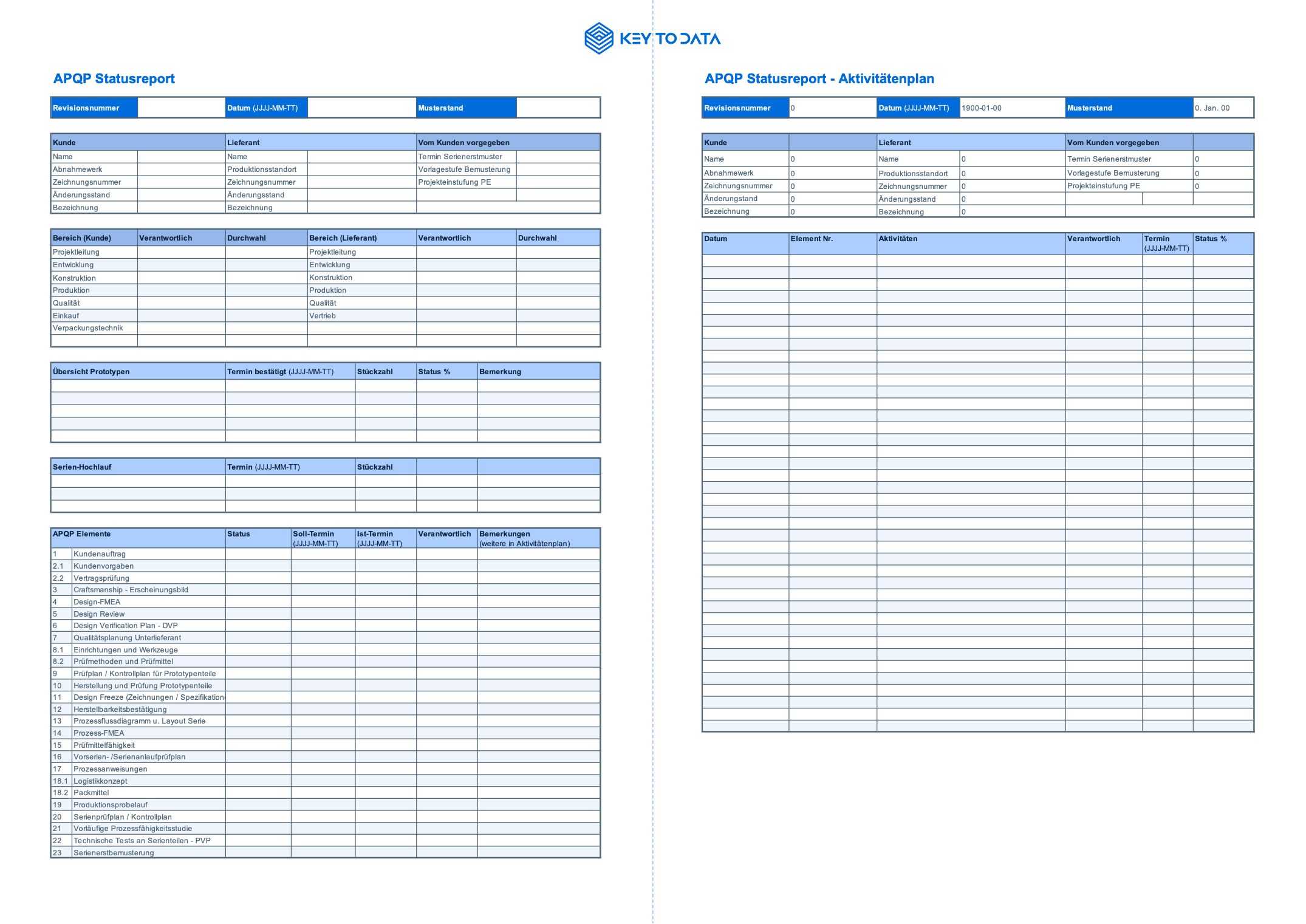
APQP Status Report and Activity Plan | Excel Template
With our free APQP Excel template, you can document the status and activities of your product quality planning project according to the status. The APQP template can be edited according to your own needs. The following entries must be made in the template:
APQP Status Report (Status Report)
- Stand
- Customer and supplier data
- Contact details of the responsible persons
- Prototype overview
- Series ramp-up
- APQP elements with status, deadlines and responsible persons.
APQP Action Plan
- Stand
- Customer and supplier data
- Activities with assignment to APQP element with deadline, responsible person and action status.
Basics
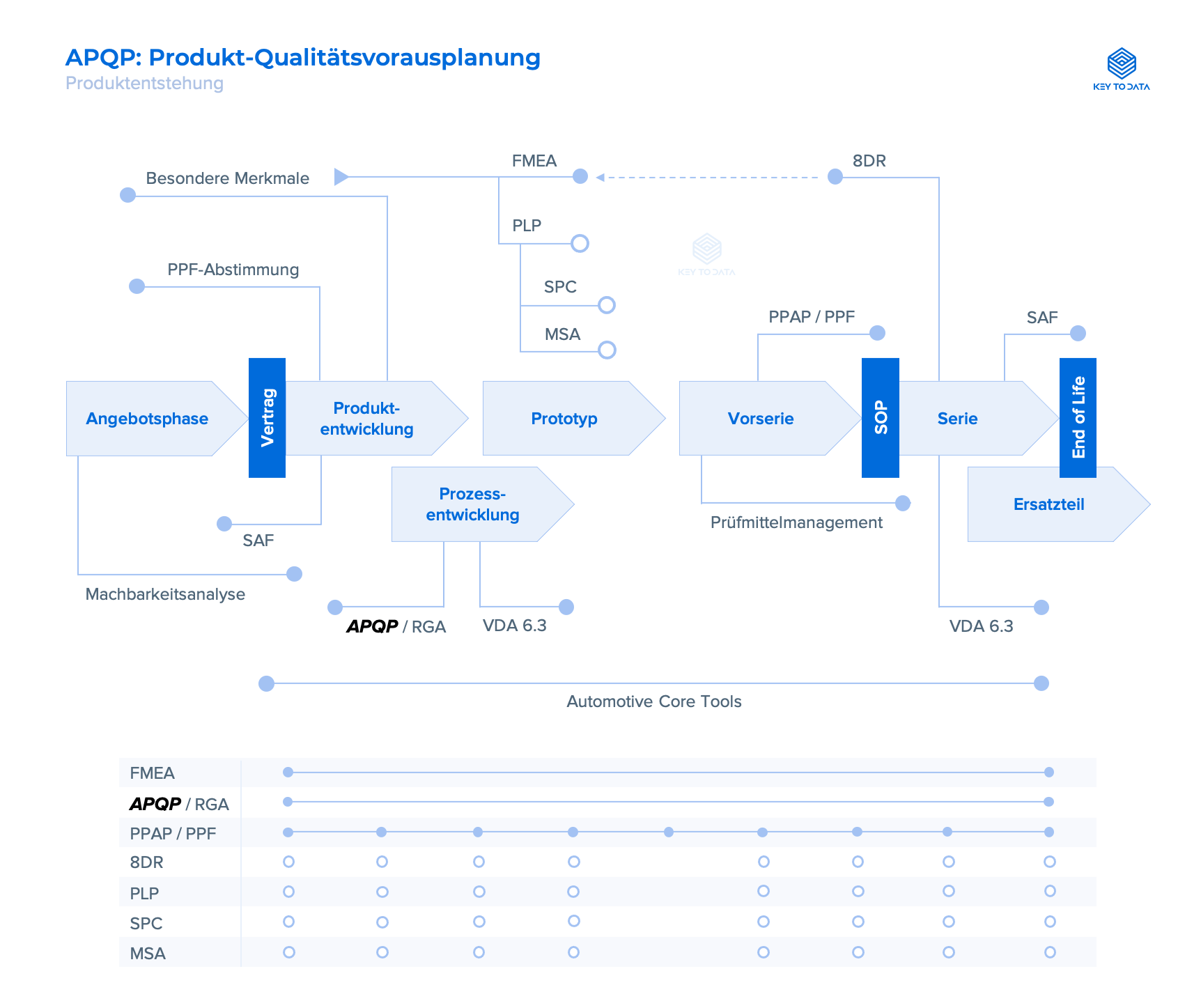
The structured process of advance product quality planning uses standardised methods (e.g. FMEA, QFD, QM plan) to ensure that the required process steps are finalised on time and that the product is satisfactory for the customer. The time sequence, the application of methods and the execution of the individual steps can vary. The result of APQP is the basis for the preparation of QM plans.
Activities at APQP
An interdisciplinary team (CFT = Cross-functional Team) consisting of experts from design, purchasing, production, logistics, supplier, QA (quality assurance) and marketing carries out the techniques described in the APQP reference manual to ensure that the products meet customer requirements. These primarily include:
- Key Characteristics: Development and definition of special features. Special process control measures may need to be initiated for these features (e.g. specifications, FMEA).
- Feasibility analysis: Conduct and document a manufacturability review with the supplier (e.g. material suitability, design, process, CPK/CMK analysis).
- FMEA: For early prevention of defects, the special features are carried out with process FMEAs (PFMEA).
- Control Plan (QM Plan): Creation of QM plans for the respective phases (prototype, pre-series, series) and at the level of assemblies, sub-assemblies as well as individual parts.
Provided that the customer does not waive them, they are provided to the customer. The APQP process has been extended by some car manufacturers by specifying the specifications in more detail.
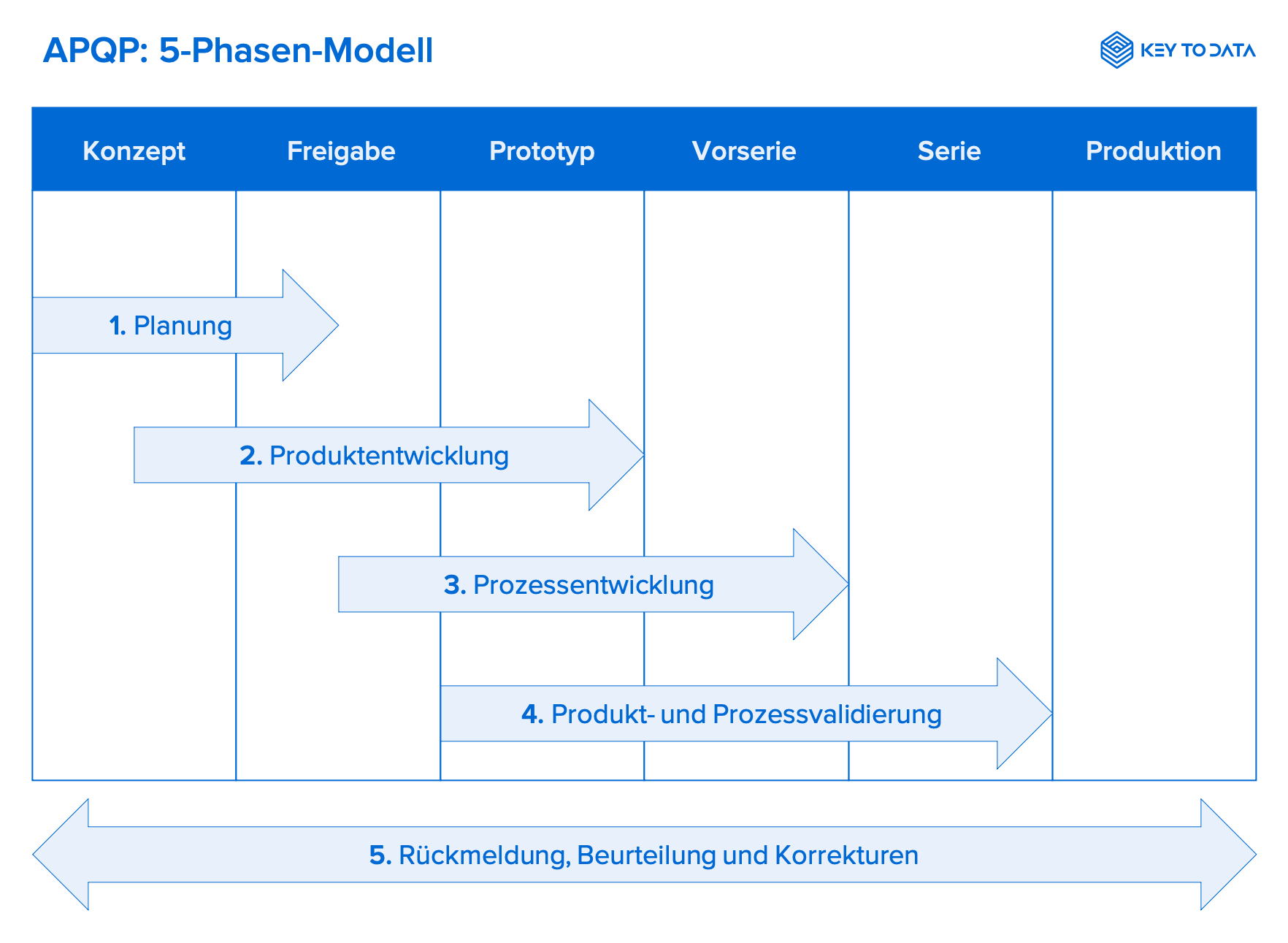
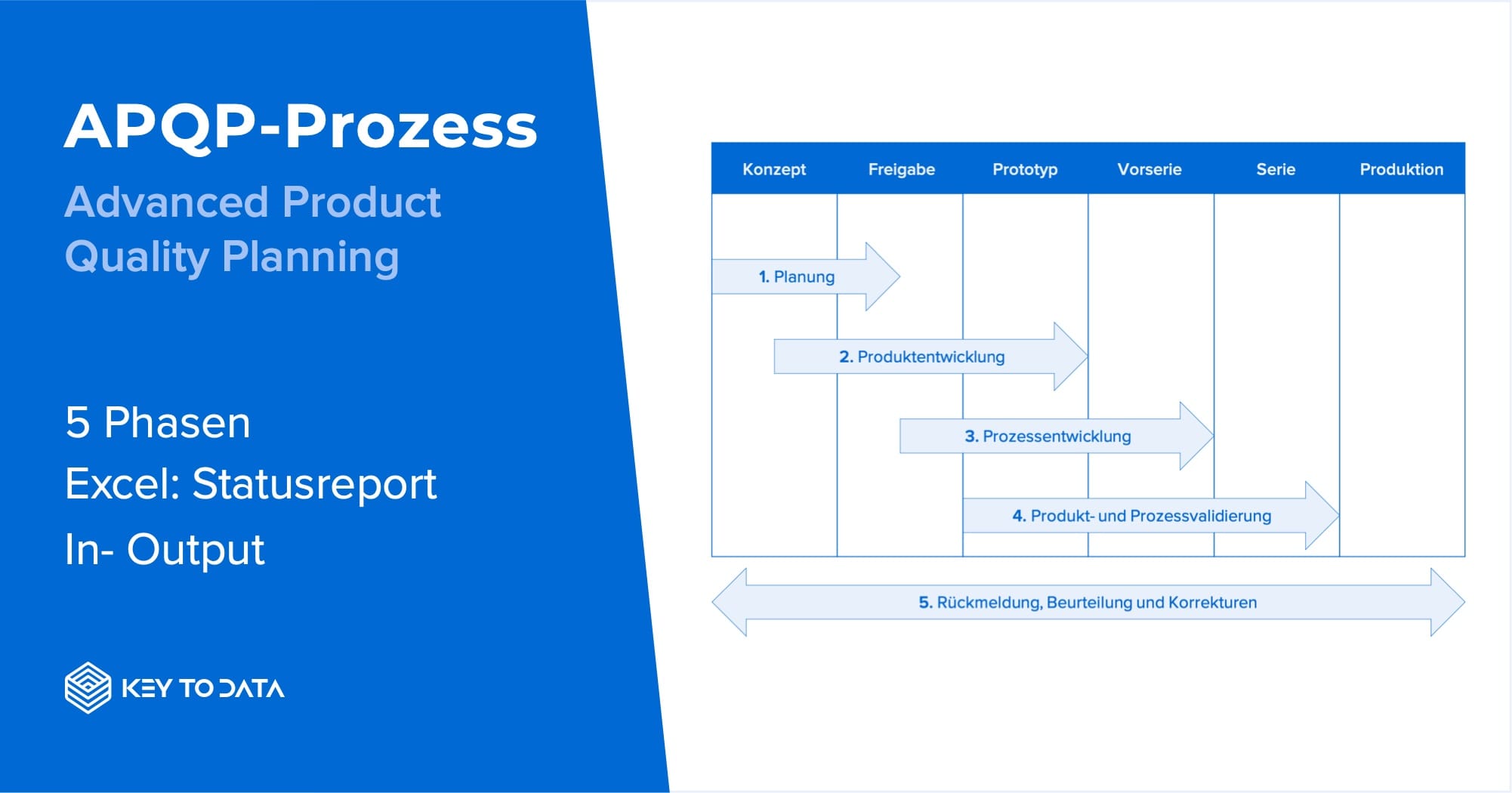
APQP: 5 phases
In this respect, APQP is an expression of the fact that quality is not only regulated and validated later in series production, but already during the definition and development of a product. Since 75% the error arise in the development and planning phase of the product, the avoidance of errors comes to the fore. To ensure the correct implementation of the APQP, this process is divided into five phases. Here, the results of the output represent the specifications of the input of the respective subsequent phase.
Diagram of the 5 phases: APQP process
1. planning
Ensure that the needs and expectations of the client are understood. In addition, the framework conditions of the project are defined. Possible work results: Requirements specifications, reliability and quality objectives. Methods such as Quality Function Deployment (QFD) can be applied here.
Input and output of phase 1
| Specifications 1. customer vote - Market studies - Warranty services - Quality information - team experiences 2. business plan / marketing strategy 3. product process benchmark data 4. product process assumptions 5. product reliability tests 6. customer details |
Results 1. design goals 2. reliability and quality targets 3. preliminary parts list 4. preliminary process flow diagram 5. provisional list of special product and process features 6. requirements specification / specifications 7. management support |
2. product development
The goal here is to develop a manufacturable design for the components. Aspects of manufacture and assembly must also be evaluated (DFMA = Design for manufacture and assembly). Possible work results can be e.g.: product FMEA, prototype or control plan (production control plan).
Input and output of phase 2
| Specifications 1. design goals 2. reliability and quality targets 3. preliminary parts list 4. preliminary process flow diagram 5. provisional list of special product and process features 6. requirements specification / specifications 7. management support |
Results 1. design FMEA 2. construction suitable for production and assembly 3. design test 4 Design Review 5. prototypes QM plan 6. technical drawings 7. technical specifications 8. material specifications 9. drawing and specification changes 10. demand for new equipment, tools and facilities 11. special product and process features 12. requirements for measuring, inspection and test equipment 13. team commitment regarding manufacturability 14. management support |
3. process development
Even though phase 3 also deals with product design, the focus here is already on process development. The goals are: Development of effective production systems, ensuring capable machines/plants and processes. Possible work results can be e.g.: process flow charts, process FMEA (PFMEA), characteristics.
Input and output of phase 3
| Specifications 1. design FMEA 2. construction suitable for production and assembly 3. design test 4 Design Review 5. prototypes QM plan 6. technical drawings 7. technical specifications 8. material specifications 9. drawing and specification changes 10. demand for new equipment, tools and facilities 11. special product and process features 12. requirements for measuring, inspection and test equipment 13. team commitment regarding manufacturability 14. management support |
Results 1. packaging standards 2. evaluation of the product-process-QM system 3. process flow diagram 4. plant structure plan (layout plan) 5. feature matrix 6. process FMEA (PFMEA) 7. pre-series QM plan 8. process work instructions 9. plan of the test equipment Capability tests 10. plan of the preliminary process capability studies 11. packaging specifications 12. management support |
4. product and process validation
In this phase, the focus is on ensuring that the manufacturer's processes deliver products that meet the customer's requirements (validation of the manufacturing process). Possible work results can be e.g.: test run results, measurement system analysis (MSA) and finally a sampling according to the customer's requirements. PPAP (Production Part Approval Process).
Input and output of phase 4
| Specifications 1. packaging standards 2. evaluation of the product / process QM system 3. process flow diagram 4. plant structure plan (layout plan) 5. feature matrix 6. process FMEA (PFMEA) 7. pre-series QM plan 8. process work instructions 9. plan of the test equipment Capability tests 10. plan of the preliminary process capability studies 11. packaging specifications 12. management support |
Results 1st production trial run (0 series) 2. test equipment Capability tests 3. preliminary process capability studies 4. production part approvals according to PPAP (AIAG) 5. product confirmation tests 6. evaluation of the packaging 7. series QM plan 8. completion and release of quality planning 9. management support |
5. feedback, assessment and corrective action
Phase 5 deals with permanent feedback as well as evaluation and corrective actions during the complete APQP process. The core objective here is the long-term fulfilment of customer requirements and the reduction of variation within production. A possible result of the work could be minimised variation in the production processes. Quality control charts (QC charts) and statistical methods can be used to determine and calculate this. The most frequently used method is SPC (Statistical Process Control).
Input and output of phase 5
| Specifications 1st production trial run (0 series) 2. test equipment Capability tests 3. preliminary process capability studies 4. production part releases according to PPAP 5. product confirmation tests 6. evaluation of the packaging 7. series QM plan 8. completion and release of quality planning 9. management support |
Results 1. reduction of dispersion 2. increasing customer satisfaction 3. improving delivery reliability and customer service |
Advantages of APQP
The APQP process offers the following advantages:
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Permanent improvement of products and processes throughout the product life cycle
- Constant exchange of information between customer and supplier
- Increased transparency and planning security.
These benefits are achieved through:
- Necessary changes are recognised early
- Cost-intensive changes shortly before the launch are avoided
- Changes that can no longer be avoided are successfully implemented
- On-time and cost-optimised product.
Disadvantages of APQP
The following negative aspects should be noted:
- Elaborate
- Employees must be trained
- The composition of the team can be difficult, as its members must have extensive knowledge of the production process.
Aims of the AIAG APQP model
What are the primary objectives of the APQP process?
- Minimising quality risks during product launch
- Permanent improvements
- Achieving budget and cost targets.
How are these goals achieved?
- Effective communication
- Adherence to deadlines
- No or minimal quality problems
- Flawless products.
Related articles:
What is the difference between PPAP and APQP?
What is PPF? (DE)
What is an EMPB?
What is a PSW?
PPAP Excel-Template
Free of charge | English | Complete
50% time saving in Inspection Report generation. Publish Inspection Reports according to VDA, PPAP, AS9102 or custom templates.
Free access for 14 days
Inspection reports in minutes, not hours
- Free training & support
- Full functionality